Environmental and social issues have been on the agenda of companies, governments, and NGOs for some years now. Therefore, much has been done to reduce environmental impact and improve the quality of life of people. Recently, entrepreneurship is emerging as a new forum within which sustainability issues are being addressed. Entrepreneurship has the potential to create value within each of the three dimensions of sustainability while boosting innovation though new products, services, and business models.
Sustainability is a broad and complex concept. For some it speaks to ecology and protection of natural resources. For others it refers to sustained economic progress or, conversely, for social issues and with a focus on development and support of the most disadvantaged. For still others, it is a combination of these. Few see the potential of value creation to contribute toward sustainability. However, sustainability is all this, and more.
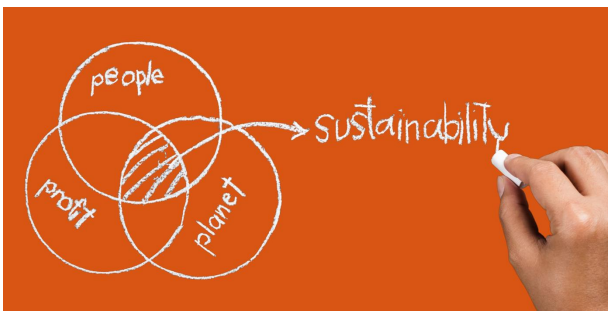
Sustainable Development is the balance between environmental, social, and economic development.
SUSTAINABLE BUSINESS SOLUTIONS:
Entrepreneurs are someone with the capacity to identify and exploit opportunities. They have ideas and make them happen. It takes commitment and perseverance to achieve this.
However, it can be very rewarding to contribute by delivering solutions that create environmental and social value and at the same time do this in a manner that is self-sustaining from an economic perspective. Sustainable entrepreneurship aims to solve social and environmental problems by applying business principles.
This is accomplished through providing sustainable business solutions that are characterized as:
1. Solutions for one specific social and/or environmental problem.
Such solutions address a problem that is clearly identified and acknowledged by. The impact of the solution can be quantified in relation to the environmental or social impact that the solution addresses.
2. Clearly defined business models.
The business model is intended to create and capture value. In the case of sustainable solutions, we talk about creating social and environmental value as well as economic value. In other words, sustainability refers to the question of how to introduce a solution to the market, how to offer value and transform the solution into financial returns while maintaining core sustainability objectives.
3. Scalable. Scalability is crucial in a start-up that aims to create impact.
In the field of sustainability, solutions that are scalable, capable of growth and able to self-support this growth are not only crucial, but also that they are relevant to a variety of contexts and markets. The scalability of a solution is the most important aspect of creating impact and value.
4. Inspire others to contribute or trigger action among others to develop their own solutions.
A good sustainable business solution inspires others to contribute to developing the idea and/or inspire others to develop their own version of the solution that adapts to other contexts. If a business solution is outstanding, one can expect that many people will be interested in joining the idea, or in developing similar solutions.

IDENTIFYING OPPORTUNITIES
There is no straightforward way to identify opportunities for the development of sustainable entrepreneurial solutions. Below are illustration of some practices and exercises that will help in identifying opportunities.
It is recognized that business opportunities are timely, attractive, durable, and are attached to a product or service that creates value for the user. In the case of sustainable entrepreneurship, opportunities are also impact-driven, as they aim to create impact through creating environmental and/or social value.
Products that represent an opportunity are efficient, empowering, and non-toxic:
• Efficient: products that require fewer resources to deliver a basic or enhanced functionality than existing alternatives. This category of products includes consumer electronics that are more energy efficient, or mobility solutions that are more fuelefficient. Those opportunities create value both for the environment (reduced consumption of resources) as well as for the user (reduced cost of ownership).
• Empowering: functional products that allow the user to be productive and “make things”. Think of power tools for instance; they allow people to build things. However, the term “empowering” is broader than that. A clean and durable light bulb is an empowering tool for someone that has a business in a village where there is no energy grid since the business can operate after the sun has set. Empowering products might be focused on providing social, rather than environmental value.
• Non-toxic: environmental and social impact might be also created by finding alternatives to existing products that require the use of toxic components to deliver functionality. The opportunity here is to aim for non-polluting or non-toxic products. Examples of this include cleaning products, batteries, or electronic components.
FROM IDEA TO SOLUTION
The application of Design Thinking plays crucial role in transforming the idea to the solution. The design thinking is a practice based on the method and sensitivity of design to develop solutions that meet user needs and create business opportunities. Design Thinking promotes a focus on user observation, visualization, prototyping of ideas, and iterative development of product solutions through user testing with the goal of maturing potential solutions.
Here the Design Thinking is used as a way to identify and develop opportunities. There are other ways to achieve the same results; however, it is said that the design thinking has significant potential owing to its practical and experimental approach, especially in the field of ecoinnovation which is dominated by learning-by-doing. Design Thinking is presented here as an alternative to traditional analytical thinking with the intent of providing a more intuitive way of thinking. Design Thinking can also be defined as an approach to innovation that combines a specific set of practices, attitudes, and cognitive processes involving several steps (e.g. Getting to know the user, Development of ideas, Prototyping; thinking by building and Iterating.

